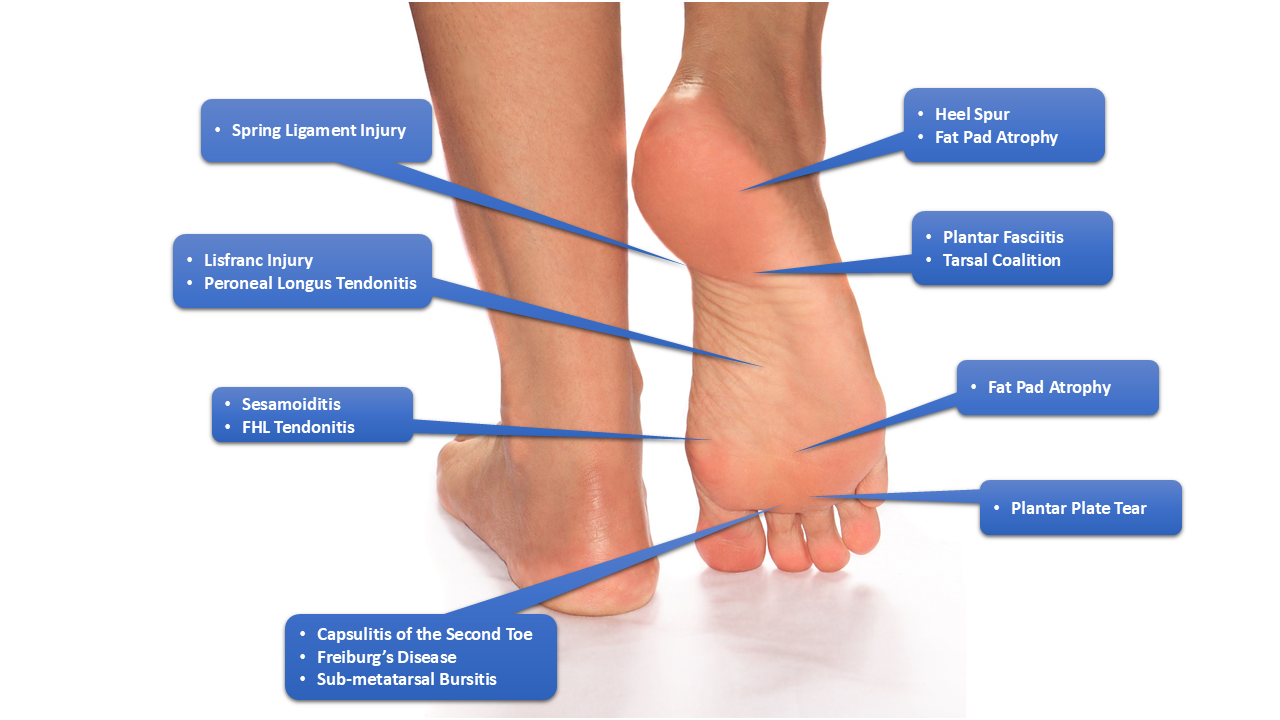
Foot pain can affect anyone, from athletes to office workers, and can seriously interfere with daily activities. Whether the discomfort starts in your heel, arches, ball of the foot, or toes, understanding the cause is essential for proper treatment. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the most common sources of foot pain from heel to toe—along with expert tips for relief and prevention.
The heel is one of the most common areas where foot pain originates. Since it absorbs much of your body weight during walking or running, even minor issues can cause major discomfort.
Plantar fasciitis is the inflammation of the thick band of tissue (plantar fascia) that runs along the bottom of your foot and connects your heel bone to your toes. It’s the leading cause of heel pain, especially in the morning or after long periods of standing.

Heel spurs are calcium deposits that cause a bony protrusion on the underside of the heel bone, often associated with plantar fasciitis.
Arch pain can result from a variety of structural or muscular issues. Since the arch acts like a spring, distributing body weight, any misalignment can lead to chronic pain.
People with flat feet often experience strain in their arches due to the lack of proper support.
This condition affects the tendon that supports your arch and can cause your foot to flatten over time.
The ball of your foot absorbs a lot of pressure during movement. If pain develops here, it’s often due to overuse, improper footwear, or nerve issues.
Metatarsalgia is inflammation and pain in the ball of the foot, often from high-impact activities or poorly fitting shoes.
This is a thickening of tissue around a nerve between the toes, commonly the third and fourth toe.
Pain in the toes can arise from structural deformities, injuries, or underlying conditions like arthritis or gout.
A bunion is a bony bump at the base of the big toe, causing the toe to angle inward.
A hammertoe occurs when the toe bends abnormally at the middle joint, often due to tight shoes or muscle imbalance.
Gout is a form of arthritis that can cause sudden, intense pain in the big toe joint due to uric acid buildup.
If your foot pain persists for more than a few days, interferes with daily activities, or worsens over time, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider or podiatrist. Ignoring chronic foot pain can lead to long-term damage or more invasive treatments later.
Wear shoes that support your arch, cushion your heel, and offer enough toe room. Avoid high heels and flip-flops for long-term wear.
Excess body weight increases pressure on your feet. A balanced diet and regular exercise can help prevent strain and injury.
Regularly stretch your calves, Achilles tendons, and foot muscles. Strengthening exercises can improve alignment and stability.
Don’t wait for holes to appear. If the soles or insoles are worn down, they no longer offer support or shock absorption.
Custom or over-the-counter orthotic inserts can provide additional support and relieve pressure from problem areas.
Foot pain is more than just a nuisance—it’s your body’s way of signaling a deeper issue. From heel to toe, identifying the specific source of discomfort is the first step toward recovery. Whether you’re dealing with plantar fasciitis, bunions, or nerve pain, there are effective treatments available. Don’t ignore persistent foot pain—address it early to stay active, mobile, and pain-free.