Knee pain is one of the most common musculoskeletal complaints affecting people of all ages. Whether you’re an athlete, a busy professional, or a retiree, knee discomfort can interfere with your daily activities and reduce your quality of life. In this guide, we’ll explore the major causes of knee pain, common symptoms, and solutions that can help you find relief.
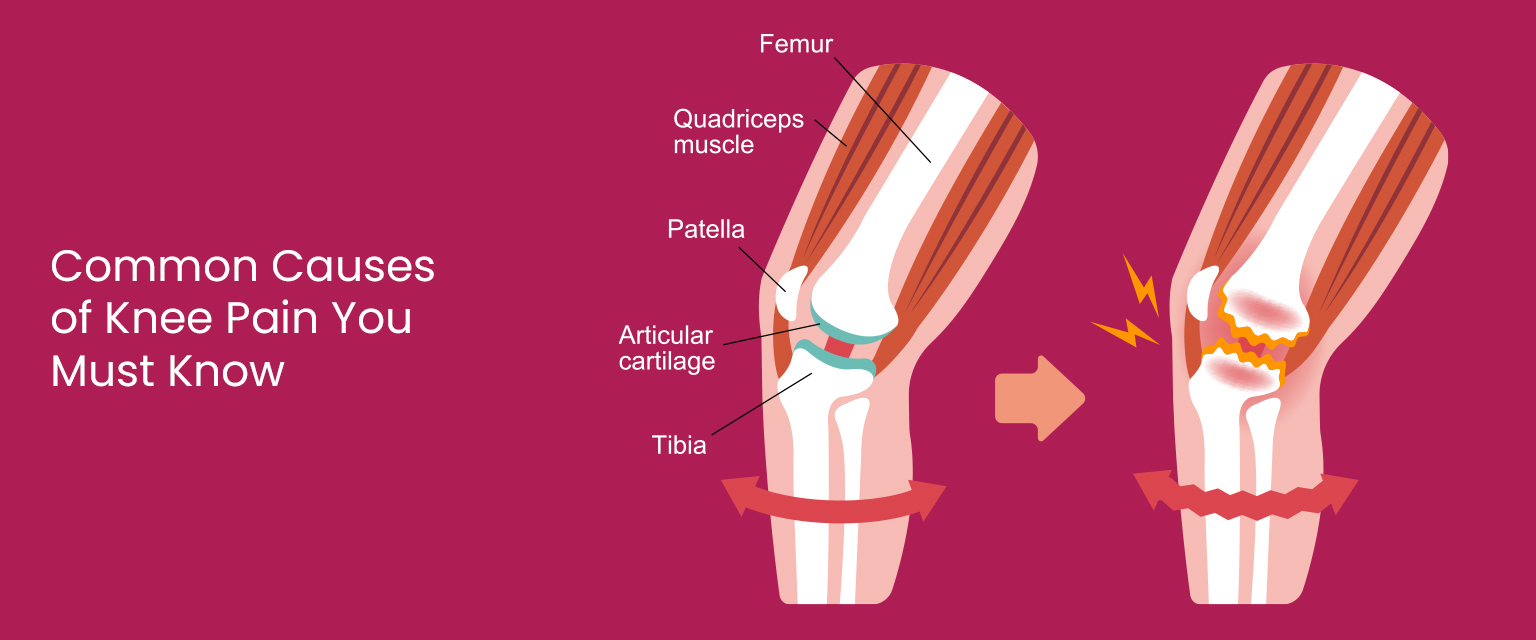
The knee is a complex joint that bears a significant amount of your body weight during everyday movements like walking, running, and climbing stairs. It is composed of bones, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons—all of which can be injured or inflamed. The high use and vulnerability of this joint make knee pain an unfortunately common issue.
There are numerous causes of knee pain, ranging from sudden injuries to long-term wear and tear. Understanding the root cause is essential for determining the right treatment path.
Ligaments are bands of connective tissue that stabilize the knee. The most commonly injured ligaments include:
The meniscus is a rubbery cartilage that acts as a cushion between the femur and tibia. A sudden twist or overuse can cause tears, leading to pain, swelling, and limited motion.
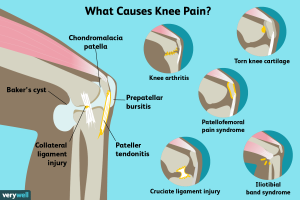
Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis affecting the knee. It occurs when the cartilage gradually wears down, causing pain, stiffness, and swelling. This condition usually develops with age and is more common in individuals over 50.
This autoimmune disease causes inflammation in the joints, including the knees. Unlike osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis can affect both knees simultaneously and may come with fatigue and systemic symptoms.
Also known as “jumper’s knee,” this condition is caused by inflammation of the tendon connecting the kneecap to the shinbone. It’s common among athletes in jumping sports like basketball and volleyball.
Bursae are small fluid-filled sacs that reduce friction in the knee. When inflamed, they can cause pain and swelling. Knee bursitis is often caused by repetitive kneeling or trauma.
This condition affects the iliotibial band, a thick band of tissue that runs along the outside of the thigh. It’s common in runners and cyclists and causes pain on the outer part of the knee.
Trauma such as falls or accidents can lead to fractures of the kneecap or dislocation of the knee joint. These injuries are usually severe and require immediate medical attention.
These are forms of arthritis caused by crystal deposits in the joint. Gout is due to uric acid crystals, while pseudogout involves calcium pyrophosphate crystals. Both conditions can cause sudden, severe knee pain and swelling.
While symptoms can vary depending on the cause, some of the most common signs of knee problems include:
If you experience these symptoms for more than a few days or if they worsen over time, it’s essential to seek medical advice.
You should consult a healthcare provider if:
This is a first-line treatment for acute injuries and minor flare-ups. It helps reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
A physical therapist can develop a personalized exercise plan to strengthen the muscles around the knee, improve flexibility, and restore function.
Over-the-counter NSAIDs like ibuprofen can help reduce inflammation. In some cases, your doctor may prescribe stronger pain relievers or corticosteroid injections.
Braces, crutches, or orthotic shoe inserts can offload stress from the knee and aid in recovery.
In severe cases—such as torn ligaments or advanced osteoarthritis—surgical intervention like arthroscopy or knee replacement may be necessary.
While not all causes of knee pain can be prevented, adopting the following habits can reduce your risk:
Knee pain can significantly impact your daily life, but understanding its causes is the first step toward effective treatment and prevention. From sports injuries to chronic joint conditions, early diagnosis and proper care can make all the difference. If you’re experiencing persistent or severe knee pain, don’t ignore it—consult a medical professional for a tailored treatment plan.