Foot pain is a common problem that can range from mild discomfort to severe, debilitating conditions. While many causes of foot pain can be managed with home care and lifestyle adjustments, there are important situations where seeing a podiatrist—the medical specialist for feet—is essential. Knowing when to seek professional help can prevent complications, speed up recovery, and improve overall foot health. In this article, we’ll explore the signs that indicate you should see a podiatrist for foot pain, common conditions they treat, and what to expect during your visit.
A podiatrist is a healthcare professional trained specifically to diagnose and treat disorders of the foot, ankle, and lower extremity. They can address a wide range of issues, including injuries, infections, deformities, chronic conditions, and pain management. If you experience persistent or severe foot pain, a podiatrist can offer expert guidance and treatment options tailored to your needs.
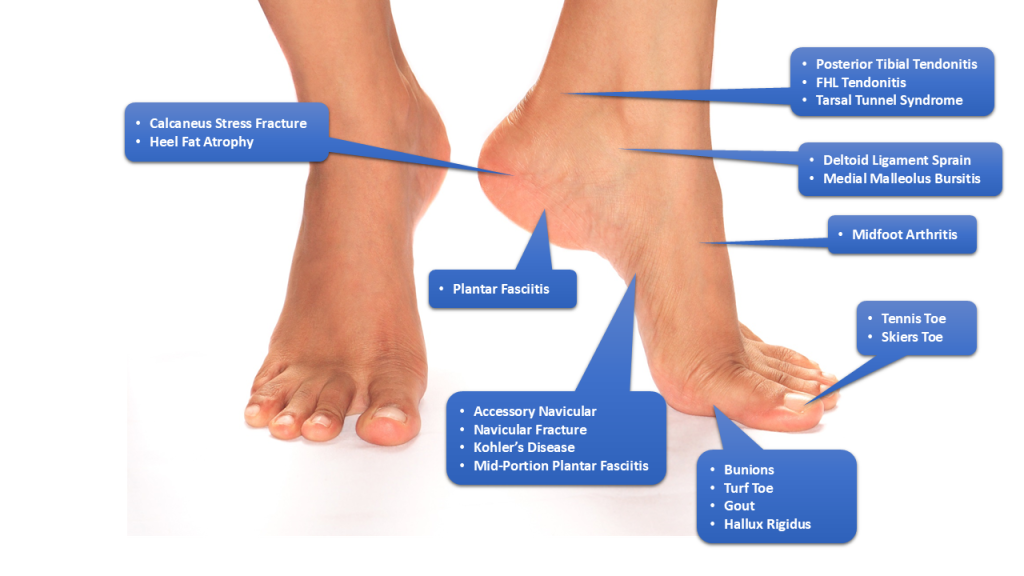
Foot pain can stem from many causes, some of which demand medical attention. Below are the common conditions that often require evaluation by a podiatrist.
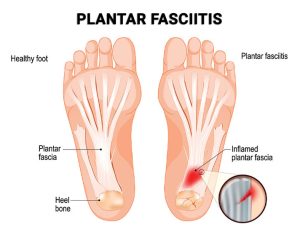
Plantar fasciitis is one of the most frequent reasons patients visit a podiatrist. It involves inflammation of the plantar fascia, the thick band of tissue connecting your heel to your toes. The resulting heel pain is often worst in the morning or after prolonged standing.
Bunions, hammertoes, and other deformities can cause significant pain and impact your ability to wear shoes comfortably.
Sprains, fractures, and other injuries need professional diagnosis to ensure proper healing and prevent long-term damage.
Numbness, tingling, burning sensations, or sharp shooting pains can indicate nerve issues such as peripheral neuropathy or Morton’s neuroma.
People with diabetes are at higher risk of foot infections, ulcers, and poor circulation. Regular podiatric care is vital to prevent complications.
Fungal infections (like athlete’s foot), ingrown toenails, warts, and other skin problems often require specialized treatment.
Some symptoms warrant urgent medical evaluation to prevent serious consequences.
If you experience sudden, intense pain or swelling in your foot or ankle, it could signal a fracture, deep vein thrombosis, or severe infection.
Non-healing sores, especially in people with diabetes or poor circulation, can lead to serious infections requiring immediate podiatric care.
Numbness, weakness, or inability to move your foot or toes needs prompt evaluation to diagnose nerve or vascular problems.
When you visit a podiatrist for foot pain, the evaluation typically includes:
Your podiatrist will ask about your symptoms, lifestyle, activity level, and any previous injuries or medical conditions.
This involves assessing the foot’s structure, alignment, range of motion, and areas of tenderness or swelling.
Depending on the suspected condition, imaging tests such as X-rays, ultrasounds, or MRIs may be ordered to get a clearer picture.
Treatment may include orthotics, medications, physical therapy, injections, or, in some cases, surgery. Your podiatrist will tailor the approach based on your diagnosis and goals.
While some foot problems require medical intervention, many can be prevented or minimized with good foot care habits.
Choose shoes that fit well, offer arch support, and protect your feet from injury.
Keep your feet clean and dry, trim toenails properly, and check regularly for any signs of problems.
Regular exercise and stretching improve circulation and maintain foot strength and flexibility.
Conditions like diabetes or arthritis require close monitoring and management to reduce foot complications.
Foot pain is a signal from your body that something needs attention. Knowing when to see a podiatrist can make a significant difference in your recovery and quality of life. If you experience persistent pain, injuries, deformities, or any alarming symptoms like numbness or open wounds, don’t delay seeking professional care. Early intervention by a podiatrist ensures you get the right diagnosis and treatment to keep you moving comfortably and confidently.